The X-ray tube is a crucial component of any radiological imaging system, and its performance greatly affects the quality of the resulting images. Among the various types of X-ray tubes available in the market today, the dual focus X-ray tube is one of the most widely used in medical applications. In this blog, we will discuss the key components of a dual focus X-ray tube, and how they work together to produce high-quality X-ray images.
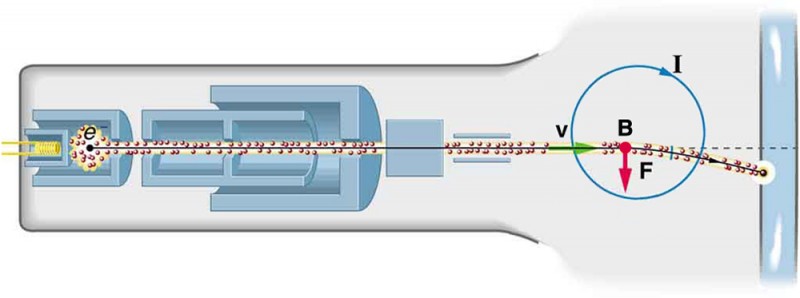
The Cathode Side of the X-ray Tube (Cathode)
The cathode side of the X-ray tube is where the X-ray production process begins. It is composed of two main components, the filament and the focusing cup.
The Filament
The filament is essentially a coil of tungsten wire that is heated using an electric current. This causes the electrons in the tungsten atoms to become excited and escape from the surface of the filament. These electrons then travel towards the anode, where they collide with the target material and produce X-rays.
The Focusing Cup
The focusing cup is a small, negatively charged cup-shaped component that surrounds the filament. Its purpose is to focus the electrons emitted by the filament towards the anode, while reducing their spread in other directions. The effectiveness of the focusing cup is determined by its size, shape, charge, filament size and shape, and the position of the filament in the focusing cup. A well-designed focusing cup ensures that the electrons produced by the filament are concentrated on a small area of the anode, resulting in a sharper and more detailed X-ray image.
The Dual Focus System
Most medical X-ray tubes have two focal spots called the dual focus. This means that there are two filaments and two focusing cups in the X-ray tube, each with a different size and shape. The smaller filament and focusing cup produce a smaller focal spot, which is used for high-resolution imaging of small body parts, such as the hands or feet. The larger filament and focusing cup produce a larger focal spot, which is used for imaging larger body parts, such as the chest or abdomen.
The dual focus system is beneficial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for greater flexibility in selecting the appropriate focal spot size for the medical examination being performed, which helps to improve image quality and reduce radiation exposure to the patient. Secondly, it extends the lifespan of the X-ray tube, since each filament and focusing cup combination can be used for different imaging purposes, reducing wear and tear on any one component.
Other Key Components of the Dual Focus X-ray Tube
Apart from the filaments and focusing cups, there are several other key components of the dual focus X-ray tube that contribute to its performance and reliability.
The Anode
The anode is the component of the X-ray tube where the electrons produced by the filament collide and create X-rays. It is typically made of tungsten or other high melting point metals that can withstand the high temperatures generated by the electron bombardment. There are typically two anode angles available in most dual focus systems, namely the large and small angles. The smaller angle is used for high-resolution imaging, while the larger angle is used for larger body parts.
The Housing
The housing of the dual focus X-ray tube is designed to protect the internal components from damage and prevent the escape of X-rays outside the tube. It is typically made of tungsten or other high-density materials that can absorb X-ray radiation. The housing also includes a window through which the X-rays can pass towards the patient.
The Cooling System
The cooling system of the dual focus X-ray tube is responsible for dissipating the heat generated by the electron bombardment and the X-ray production process. Most cooling systems use a combination of oil and air to remove the heat, while some more advanced systems use water or liquid metal.
Conclusion
The dual focus X-ray tube is an essential component of medical radiography, providing high-quality imaging while enhancing the safety and comfort of the patient. The combination of filaments, focusing cups, anodes, housing, and cooling systems work together to produce images of exceptional quality and clarity. By understanding how these components function within the X-ray tube, medical professionals can more effectively select and operate the appropriate radiology equipment, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.